How the Umami Taste Can Help Reduce Sodium in Foods
Autor(a):
Hellen Dea Barros Maluly (MALULY, H.D.B.)
Farmacéutico y Doctor en Ciencias de la Alimentación
Dirección para acceder a este CV: http://lattes.cnpq.br/2754275781355863
Published on: 10 de September de 2021
Resumo
The sodium ion is vital for the human body and also plays a crucial role in food technology. However, excessive consumption has contributed to the development of non-communicable diseases such as hypertension, cardiovascular disease, and renal disease. Consequently, it has become necessary to develop new products with reduced sodium content that do not compromise flavor. In this context, substances that provide the umami taste have been used and well received by the population.
Palavras-chaves: sodium chloride, sodium reduction, umami taste, flavor, acceptability
Sodium chloride is the most widely used salt by individuals and the food industry, primarily due to its ability to enhance flavor and its efficiency as a preservative. It helps ensure product safety and is cost-effective. It is used in meat products especially for extracting and solubilizing myofibrillar proteins, which improves texture, reduces water activity, increases osmotic pressure—and thereby inhibits microbial growth and spoilage.
The sodium ion is essential for the body, contributing to electrolyte balance and supporting membrane potential (together with potassium via the sodium/potassium ATPase) necessary for nerve impulse transmission and muscle contraction. These functions rely mainly on sodium intake through foods. Nevertheless, like any nutrient, sodium must be consumed in appropriate quantities. The World Health Organization recommends a maximum sodium intake of 2 grams per day.
Excessive sodium consumption has become problematic, especially due to high rates of hypertension, cardiovascular diseases, and renal problems observed in hospital outpatient clinics. These issues are not solely attributable to sodium intake but are also linked to unhealthy dietary habits—including high fat intake, low fruit and vegetable consumption, as well as factors such as stress and sedentary lifestyle.
Industrially produced umami taste compounds—such as monosodium glutamate (MSG), disodium inosinate, and disodium guanylate—do contain sodium, but in much lower proportions compared to sodium chloride. This is because their molecular mass is much higher. See below the mass ratio comparisons between substances and sodium percentages.
Table: Percentage composition of salt and MSG used in rice and meat preparations:
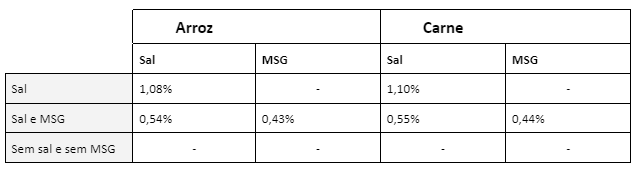

From this comparison, it is evident that umami substances can help reduce the amount of sodium in preparations. For example, one can replace a certain amount of salt (½ teaspoon) with monosodium glutamate, which is sold in its pure form in supermarkets. See the figure on the side showing how this substitution can occur without compromising flavor and can maintain sodium at appropriate levels—ensuring this essential nutrient does not adversely affect our health. After all, for health, the pleasure of eating is necessary for the hedonic moments in our lives .
References
- HALIM, J.; BOUZARI, A., FELDER, D.; GUINARD, J. The Salt Flip: Sensory mitigation of salt (and sodium) reduction with monosodium glutamate (MSG) in "Better-for-You" foods. Journal Food Science, v.85, n.9: 2902-2914, 2020.
- HENNEY J. E., TAYLOR C. L., & BOON C. S. (Eds.). Institute of Medicine IOM (Institute of Medicine) – strategies to reduce sodium intake in the United States. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press, 2010.
- HE, F.J.; CAMPBELL, N.R.C.; MACGREGOR, G.A. Reducing salt intake to prevent hypertension and cardiovascular disease. Revista Panamericana de Salud Pública, 2012.
- MALULY, H.D.B.; ARISSETO-BRAGOTTO, A.P.; REYES, F.G.R. Monosodium glutamate as a tool to reduce sodium in foodstuffs: Technological and safety aspects. Food Science and Nutrition, v. 5, n. 6, 2017, p. 1039-1048.
- ROSA, M.S.C., PINTO-E-SILVA, M.E.M., SIMONI, N. K. Can umami taste be an adequate tool for reducing sodium in food preparations? International Journal of Food Science and Technology, 2021.




